

Anemia can also be a consequence of low levels of iron, B12, or folate in the diet, along with other potential causes - including heavy or persistent bleeding. Anemia may occur when there are too few red blood cells being made in the bone marrow, or when the red cells are being destroyed by disease. If someone’s RBC, hematocrit, or hemoglobin counts are low, they are considered anemic. If results show your risk for serious side effects or complications is rising, your doctor may make a change in your leukemia treatment or prescribe other medications to address the problem. Your CBC results will help your doctor better understand how your leukemia and leukemia treatments are affecting your body. For instance, in people living with heart disease, a higher-than-normal RBC count may be normal. Although normal ranges are an expression of what is normal for the majority of healthy people, those with underlying conditions may have lower or higher ranges that are normal for them. Abnormal results can indicate an issue in the bone marrow - where blood cells are made - or a variety of other disease processes. For instance, the white blood cell differential may show an abnormal skew in WBC types. What do abnormal results mean? For any given value, a result can be too high, too low, or unusual in relation to another value. Leukemia can affect blood cell counts in various ways, as can many treatments for leukemia - such as chemotherapy and radiation. In a normal blood count, the WBC differential comprises:īasophils and eosinophils make up the remainder. There are five main types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and basophils. White blood cells are also measured by ratio of WBC types - the white blood cell differential. Platelet counts, regardless of age or gender, are considered normal at 150,000 to 400,000 per microliter. Hemoglobin is expressed in grams per deciliter (gm/dL).
The normal range of white blood cells per microliter is: The normal range of red blood cells per microliter is: However, there are general ranges for men, women, and children. On a CBC, red blood cell levels, white blood cell levels, and platelet levels are typically expressed as the number of cells per microliter of blood. Hematocrit and hemoglobin help doctors better understand how well your RBCs are functioning at carrying oxygen to the tissues of your body. Hemoglobin indirectly measures the number of red blood cells in your blood.
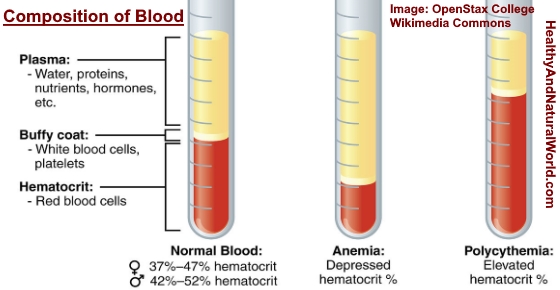
Hematocrit levels measure how much of your blood, by percentage, is currently made up of red cells. Two other aspects of blood are usually tested in a CBC: hematocrit and hemoglobin. They are small cells that gather at sites of injury and help blood clot. Platelets are also referred to as thrombocytes.They work as a first line of defense in the immune system, fighting bacteria and viruses that may enter the blood. White cells (WBCs) are also known as leukocytes.Their primary function is to carry oxygen from the heart and lungs to different parts of the body. Red cells (RBCs) are also referred to as erythrocytes.Blood is made of three main types of cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Types of Blood CellsĪ complete blood count shows the current number of cells in your blood and what types of cells they are. Here is a breakdown of what is tested for and what CBC results can tell doctors. The abbreviations that appear on a CBC results report can be confusing. A CBC is one of the most frequently run tests for people with leukemia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
